Multi-task learning and Multi-Modal learning
Published:
Multi-task Learning solves multiple tasks at one time, while exploiting commonalities and differences across tasks. Multi-modal Learning integrates and processes multiple types of data in one framework.
The following flowchart demostrate Multi-tasking and Multi-modal learning, and Multi-task, Multi-modal learning.
Multl-Task Learning: 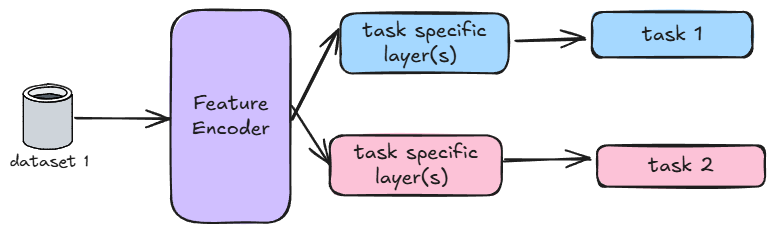
Multi-Modal Learning 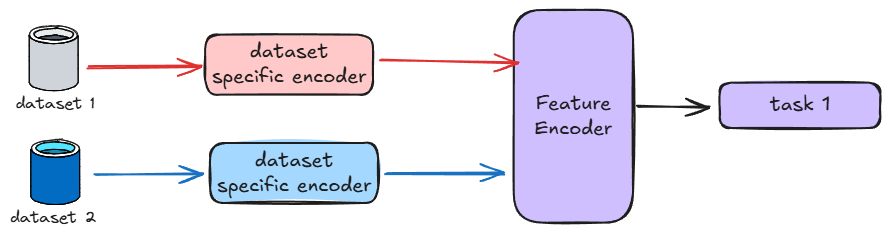
Multi-Modal & Multi-Task Learning 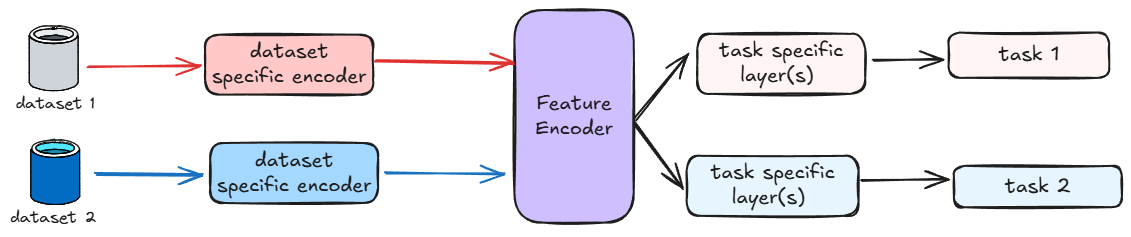
Multi-task Learning Code Sample
# multi-task learning
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
def build_multi_task_model(input_shape, num_classes):
# Input Layer
inputs = Input(shape=input_shape)
# Shared layers
x = Dense(128, activation='relu')(inputs)
x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x)
# Task 1: Regression Output
reg_output = Dense(1, name='regression_output')(x)
# Task 2: Classification Output
class_output = Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax', name='classification_output')(x)
# Build the Model
model = Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=[reg_output, class_output])
return model
# Build the model
model = build_multi_task_model(input_shape, num_classes)
# Compile the model with different losses and metrics for each task
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss={'regression_output': 'mse', 'classification_output': 'sparse_categorical_crossentropy'},
metrics={'regression_output': ['mae'], 'classification_output': ['accuracy']})
# Summary of the model
model.summary()
Multi-Modal Learning Code Sample
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# Define the shared layer
shared_layer = tf.keras.layers.Dense(32, activation='relu')
# Create two input layers
input1 = tf.keras.Input(shape=(10,))
input2 = tf.keras.Input(shape=(10,))
# seperate feature encodings
feature1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(5, activation = 'relu')(input1)
feature2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(5, activation = 'relu')(input2)
# Apply the shared layer to both inputs
x1 = shared_layer(feature1)
x2 = shared_layer(feature2)
# Further processing for each branch
x1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(16, activation='relu')(x1)
x2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(16, activation='relu')(x2)
# Combine feature maps from
concatinate_feature_map = tf.keras.layers.Concatenate()([x1, x2])
output = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation = 'sigmoid')(concatinate_feature_map)
# Create the model
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=[input1, input2], outputs=output)
model.summary()
Multi-Task and Multi-Modal Learning
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
num_classes = 2
# Define the shared layer
shared_layer = tf.keras.layers.Dense(32, activation='relu', name = 'shared_encoder')
# Create two input layers
input1 = tf.keras.Input(shape=(10,))
input2 = tf.keras.Input(shape=(10,))
feature1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(5, activation = 'relu', name = 'data1_encoder')(input1)
feature2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(5, activation = 'relu', name = 'data2_encoder')(input2)
# Apply the shared layer to both inputs
x1 = shared_layer(feature1)
x2 = shared_layer(feature2)
# Further processing for each branch
x1_output = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='relu', name = 'feature1_encoder')(x1)
x2_output = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='relu', name = 'feature2_encoder')(x2)
# Task 1: Regression Output
reg_output = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, name='regression_output')(x1_output)
# Task 2: Classification Output
class_output = tf.keras.layers.Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax', name='classification_output')(x2_output)
# Create the model
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=[input1, input2], outputs=[reg_output, class_output])
# Compile the model with different losses and metrics for each task
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss={'regression_output': 'mse', 'classification_output': 'sparse_categorical_crossentropy'},
metrics={'regression_output': ['mae'], 'classification_output': ['accuracy']})
# Summary of the model
model.summary()
